Have you received messages on Facebook pretending to be from Meta’s Business Help Center? This article will explain how scammers are exploiting small businesses and creators with phishing attempts aiming to steal account access.
Scam Overview
The Meta Business Help Center phishing scam targets Facebook and Instagram business account owners by pretending to be urgent warning messages from Meta’s real help teams citing policy violations about to result in permanent page deletion.
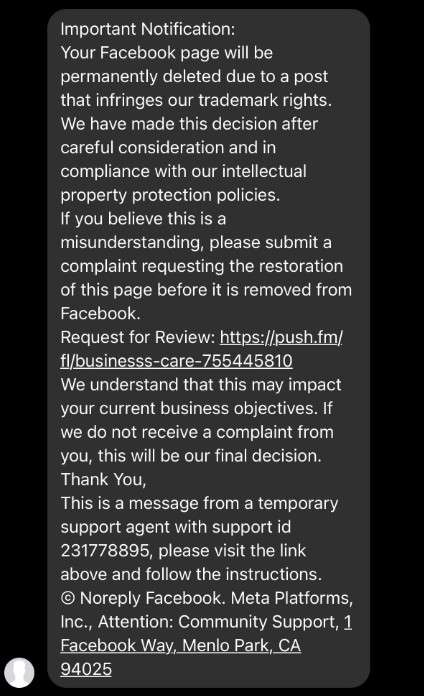
These scam messages state the recipient has 24 hours to fix issues by clicking provided links to submit account reviews before termination. However, the links lead to sophisticated fake login portals that capture entered credentials, allowing scammers to hijack access.
Once inside a business account, criminals can ravage brand trust and assets built over years by impersonating identities followers rely on for legitimate guidance, stealing valuable audience data, running fraudulent ads earning illicit profits, demanding ransoms from desperate owners locked out, and more damaging exploits.
By instilling fears of losing integral marketing platforms connecting enterprises to target demographics, clever social engineering overrides logical skepticism that would otherwise reveal inconsistencies exposing the scam’s fundamentally fraudulent nature.
Delivery Strategies
This business-focused phishing campaign reaches recipients via:
- Facebook Messages: Direct alerts to account inboxes pretending to source from Meta’s verified Business Help Center. These evade initial spam detection by first establishing connections before deploying urgent threats.
- Email Notifications: Messages containing Facebook branding and official warning formats are sent to account emails on file, often using “Critical Account Alert” subject lines to entice opening.
- Text Messages: SMS texts sent to linked mobile numbers pretend to be from Meta support teams, identifying recipients by name and citing removal justifications to seem credible.
Regardless of contact medium, messages spoof verified sender details like Meta’s trademarked logos and Business Help Center channel name to impersonate trusted authority.
Financial Incentives For Hijacking Access
By stealing business account credentials through social engineering rather than technical attacks directly against Facebook’s hardened infrastructure, scammers create lucrative monetization pathways by:
- Ransom Demands: Further extorting locked-out business owners unable to afford severe brand damages if they permanently lose meticulously constructed marketing funnels. Payments are demanded in anonymous cryptocurrencies.
- Fake Ad Campaigns: Placing high-value ads linked to external phishing websites, earning affiliate payouts from successfully tricked site visitors. Stolen payment methods on compromised accounts fund these fraudulent promotions.
- Harvesting Follower Data: Extracting minable audience demographics data like personalized interests, contact info and behavioral analytics built via years of genuine content marketing efforts – then selling this data on black markets.
But non-monetary motives like spreading political disinformation also prove profitable once trusted business profiles get infiltrated by malicious actors.
Targeted Account Types
While any registered business account faces this phishing threat, tailored versions often focus high-influence targets like:
- Thought Leaders: Compromising social profiles of public intellectuals, motivational speakers and trending experts allows directly impersonating their brands by contradicting established positional stances through fake statements designed to deteriorate credibility on hot topics their followership cares about.
- Consumer Brands: Infiltrating consumer businesses built on lifestyle messaging lets scammers directly interact with loyal customer bases to shatter assiduously crafted brand images reflecting company values and ethical standards around transparency.
- Ecommerce Sellers: Stealing login data for popular online storefronts allows scammers to destroy years of perfected digital marketing funnels by sabotaging trust signals driving recurring sales through genuine relationship building.
But with wider societal countermeasures strengthening protections around accountable thought leadership, collective community resilience denies disruptive schemers from achieving their disruptive aims.
How The Scam Works
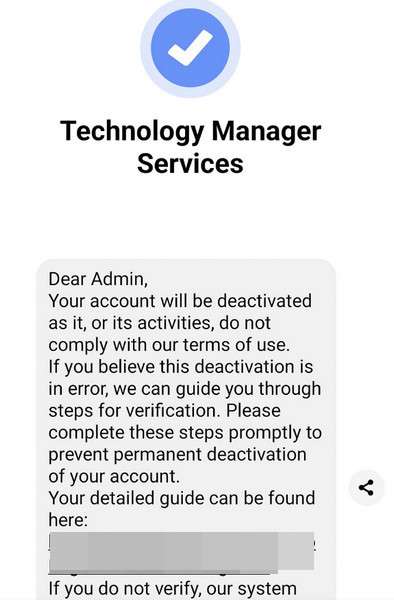
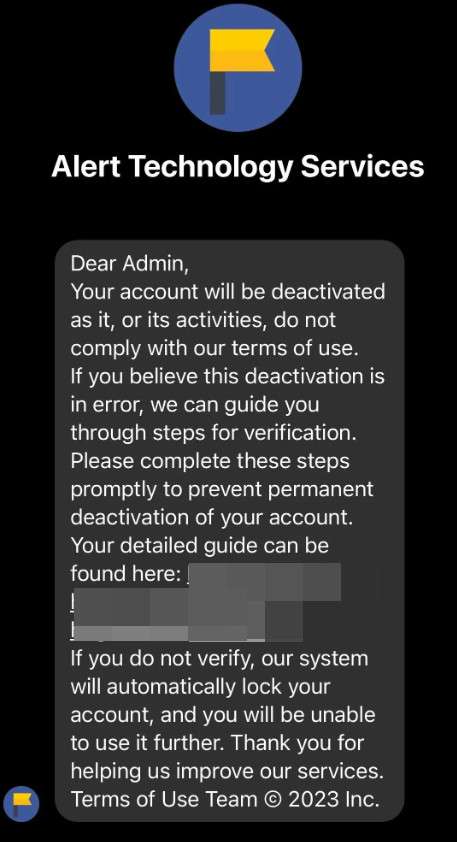
The Meta Business Help Center scam starts by sending business owners an unsolicited Facebook Message such as:
Meta Business Help Center – Urgent Notice
Your Facebook and Instagram business account showing repeated Community Standards violations around prohibited content. As per our repeat offender account termination policy, your pages will be permanently disabled within 24 hours unless issues are verified and corrected by visiting: http://accountviolation.com/fbreview
The message claims to come from Meta’s real Business Help Team channel with warnings based on Facebook’s genuine Community Standards policies prohibiting dangerous regulated goods sales, hate speech, bullying behavior, sexually explicit content, and other guideline violations.
By citing these reasons for pending account deletion, scammers aim to seem credible on first glance by reflecting common problems real business accounts experience around compliance.
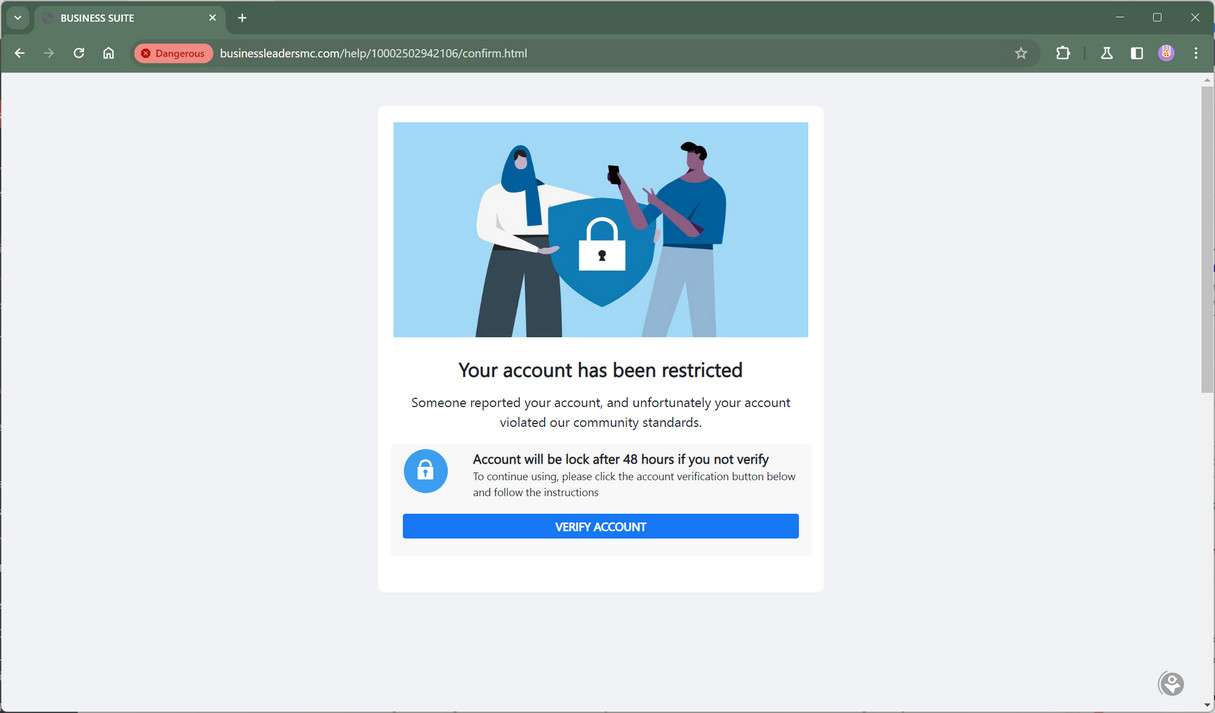
The message stresses urgent action within 24 hours, linking to an official-looking account reviewal portal. However, that links to advanced phishing sites capturing logged-in Facebook credentials from unsuspecting business owners before granting access to their accounts.
Once inside a compromised account, scammers can:
- Impersonate Brands: Make posts contradicting company values after cultivating audience trust over years.
- Hijack Followers: Message engaged customers redirecting them towards malicious links or fake promotions from formerly trusted profiles.
- Steal Marketing Data: Access and sell valuable audience demographics and contact info to unscrupulous third-party advertisers.
- Run Fake Ads: Place high-spending ads linking external financial scams, earning payouts from stolen payment methods.
- Demand Ransoms: Further extort locked-out business owners desperate to salvage reputations built via social media.
With so much at stake around securing integral access channels connecting modern enterprises to target demographics, awareness around associated social vulnerabilities protects community prosperity.
How to Spot the Meta Business Help Center Scam
While seeming convincingly urgent at first glance, several subtle signs can reveal the Meta Business Help Center scam’s fraudulent nature:
1. Non-Specific Violation Details
Authentic warnings outline exact prohibited content shared or policies violated. Vague claims of “repeated violations” without proof indicate scam threats.
2. Inconsistent Sender Identity
Messages pretend to come from Meta’s real Business Help Center. But scrutinizing sender details reveals spoofed verified badges and channel names diverging from legitimate sources.
3. Illogical Ultimatums
Meta allows reasonable response times to most account issues before considering permanent disabling. But scam threats impose unrealistic 24-48 hour deadlines counting down to termination.
4. Stylistic Language Irregularities
Professional messages avoid awkward phrasing or grammatical mistakes. Contrastingly, scam content contains subtle linguistic tells exposing non-native English origins.
5. Suspicious Links
While incorporating Facebook’s name, scam site URLs lead to different domains lacking the SSL certificates securing legitimate Meta properties. Entering data on unencrypted pages enables credential theft.
Staying observant for these types of suspicious characteristics helps business account owners across Facebook and Instagram confidently identify and sidestep sophisticated phishing attempts aimed at jeopardizing marketing efforts by hijacking built connections with followers.
What To Do If You Have Fallen Victim
If you entered account credentials into any suspicious Meta Business Help Center warnings, your profiles may be compromised. Follow these steps to secure things:
Change Passwords
Reset the passwords for any accounts that got accessed to log out the scammers. Enable enhanced login approvals for extra security against repeat intrusions.
Review Recent Activities
Check account posts, messages, payments and ads for unauthorized changes. Remove any fraudulent items falsely representing brands that followers rely on for legitimate guidance.
Run Antivirus Scans
Scan all personal and professional devices in case embedded malware granted backdoor access for future data harvesting or distribution schemes.
Warn Connections
Inform your audience on compromised profiles that communications should be cautiously verified until account security gets regained. Apologize for the confusion while advising contacts to watch for potential misinformation spreading scams during this window.
Report Incidents
File detailed reports to Meta regarding phishing attack specifics like links, source profiles and screenshots so investigations can disrupt these schemes at scale by banning fraudulent actors and domains.
Enhance Login Protections
Ensure robust login approval policies require secondary identity verification through prompts on new devices even after changing passwords for the most resilient defense. Remain vigilant about monitoring account activities for anything unusual in the weeks ahead.
Implementing rigorous protections denies disruptive schemers from succeeding in hijacking trusted community platforms built on authentic engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions About The Meta Business Help Center Scam
This phishing scam threatens enterprises by impersonating Meta’s real business support teams citing violations risking account disabling. Outlining insights around common concerns empowers digital marketing leaders to secure vital community channels against unlawful intrusions.
Why does Meta send business accounts urgent policy violation warnings?
Meta rarely disables accounts suddenly without allowing reasonable appeal opportunities, only in cases of severe repeated legal violations. Scam warnings ignore real safeguards by demanding impossible urgent responses citing extreme overreactions like complete account deletions.
What techniques make the scam messages seem real?
Perfectly spoofing official Meta branding and channel names, citing real policy sections like “Community Standards” and even referencing recipients by name, scammers replicate authentic authority markers that dissolve under close scrutiny revealing inconsistencies.
How do scammers financially benefit from stealing business credentials?
Compromised accounts provide pathways for running fraudulent advertising campaigns earning illicit commissions, ransoming distressed owners at risk of losing their marketing investments if permanently locked out, and harvesting follower data to sell on dark web black markets.
What broader societal dangers emerge from hijacked business profiles?
Infiltrating established community trust opens avenues for spreading dangerous misinformation from perceived reputable sources, orchestrating harassment against minority groups by weaponizing follower bases, and corroding credibility of public thought leaders through fake inflammatory statements.
How can small business owners bolster Meta account protections?
Always scrutinizing unsolicited urgent warnings, enabling robust login approvals, creating unique complex passwords, restricting overexposed permissions and reporting phishing attempts fortifies defenses. Seeking official guidance for navigating complex digital policies also promotes resilience.
Bolstering public understanding around malicious efforts to exploit integral marketing platforms strengthens prosperity across interconnected community economies by upholding standards around accountability.
Conclusion
The Meta Business Help Center Facebook phishing scam threatens enterprises and creators by exploiting fears of losing integral access channels connecting them to target demographics. But recognizing associated psychological manipulation techniques allows recipients to instead identify inconsistencies and deny attention to unwanted intrusions.
Moving forward, social media account owners should scrutinize unsolicited warnings, avoid password reuse, enable enhanced authentication, and report suspicious activities. Prioritizing audience value through consistent brand standards fosters genuine engagement growth.
Equipping well-meaning communities with insights around adversarial interests aiming to corrupt consensus spaces promotes wisdom transferring practical knowledge between regular users and platform policy experts navigating increasingly digitized public infrastructure facing sophisticated fraud campaigns.



![Remove News-mapesu.com Pop-up Ads [Virus Removal Guide] 10 McAfee scam 4](https://malwaretips.com/blogs/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/McAfee-scam-4-290x290.jpg)