Have you received a text message claiming your vehicle has an unpaid parking invoice? This scam has been reported in major cities like Los Angeles, New York and Boston. The message urges you to click on a link to view and pay your invoice to avoid additional fees. However, it’s a trick to steal your personal and financial information.




Overview of the Parking Invoice Scam
This parking invoice scam starts with an unsolicited text message sent to your mobile phone. The message claims to be from a city agency, often including the city name, such as the “City of Boston” or “City of Los Angeles”.
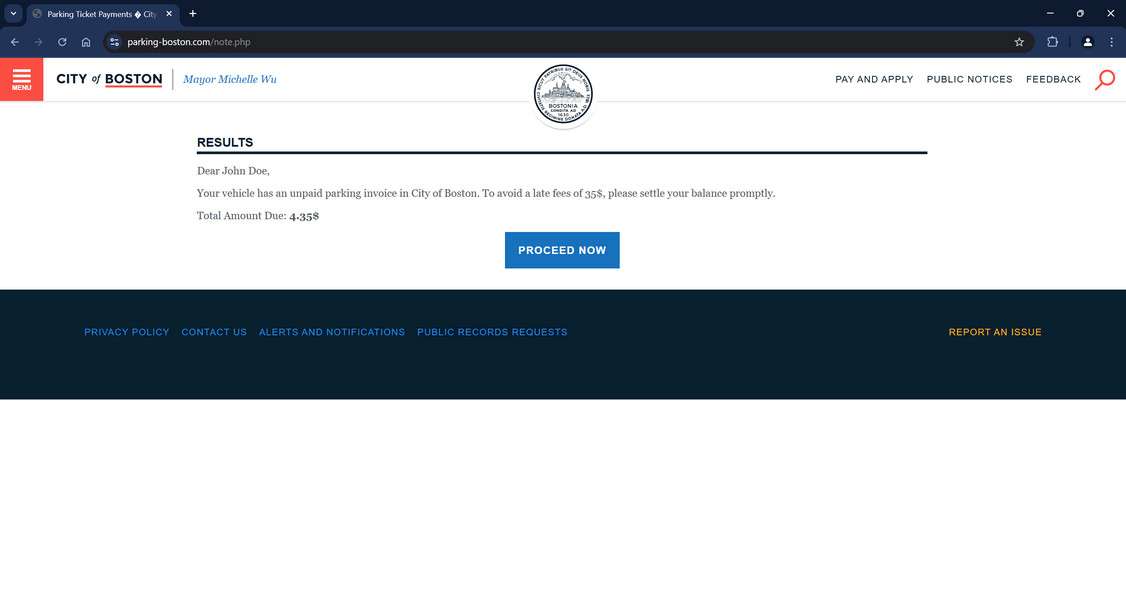
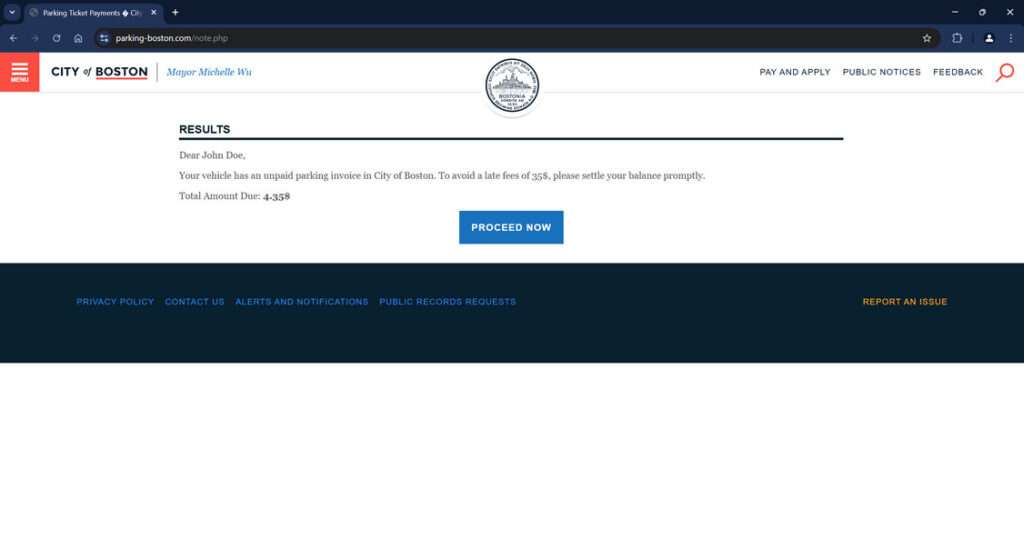
The text states that your vehicle has an unpaid parking ticket or invoice, usually for a small amount like $4.35. It instructs you to click on a link to view and pay the invoice promptly, or else face additional late fees.
However, the link does not lead to a city website. Instead, it goes to a realistic-looking but fake website designed solely to steal your personal and financial information.
The scam website will request your:
- Full name
- Birth date
- Address
- Phone number
- Email address
- Credit card number
- Security code
Armed with this information, scammers can commit identity theft or make fraudulent charges to your accounts.
This parking invoice scam takes advantage of people’s fear of incurring late fees on unpaid tickets. The urgency created by the text’s warning is meant to panic recipients into providing their info without thinking.
How the Parking Invoice Scam Works
Here is a step-by-step look at how this scam unfolds:
1. You Receive an Unsolicited Text
The scam starts with an unsolicited text sent to your mobile number. The message will look something like this:
“This is a notice from the City of Boston. Your vehicle has an unpaid parking invoice of $4.35. To avoid a late fee of $35, please settle your balance promptly. To access your file, type the following link in your browser: https://parking-boston.com/”
The text may reference different city names and various unpaid invoice amounts. But the goal is the same – to get you to click the link.
2. You Click The Link
If you click the link, it will take you to a website that looks like an official city parking or transportation website. However, the URL will be different from the actual city site.
The scam website is designed to look as realistic as possible, including official-looking seals and branding. This builds a false sense of security to keep you engaged.
3. You Are Asked for Personal and Financial Information
The website will prominently prompt you to pay the unpaid invoice, stating you must provide additional information to proceed. You’ll then be asked to input details like:
- Your full name
- Birth date
- Address
- Phone number
- Email address
After providing your personal information, you will be asked for financial information, including:
- Credit card number
- Card expiration date
- CVV security code
The website may note this is required for an instant online payment. The urgency is meant to prevent you from thinking it through.
4. Scammers Steal Your Information
Once submitted, your personal and financial information goes directly to scammers. They can then use it for activities like:
- Committing identity theft
- Making fraudulent charges on your credit card
- Accessing your bank accounts
- Taking out loans or credit cards in your name
Meanwhile, you never actually paid any parking invoice. The urgent text, fake website, and request for personal information were all an elaborate scheme to access and abuse your details for financial gain.
What to Do If You Fell For This Scam
If you responded to one of these scam parking texts and shared any personal or financial information, take these steps right away:
- Contact your credit card company – Report any fraudulent charges and cancel your current card to prevent additional charges. Request a new card with a different number be issued.
- Call your bank – Alert them to the risk of fraudulent activity and request increased monitoring of your accounts for suspicious transactions. Consider changing usernames and passwords.
- Check your credit reports – Request free credit reports from Equifax, Experian and TransUnion to catch any signs of identity theft, like unauthorized accounts or loan requests. Consider freezing your credit to block thieves from opening new accounts.
- Update account security – Change the passwords and security questions/answers for all of your financial accounts and email accounts. Enable two-factor authentication where possible.
- Watch for suspicious activity – Be vigilant about reviewing account statements, credit reports and explanations of benefits for any transactions you don’t recognize for the next 12-24 months. Report any fraudulent activity immediately.
- Report the scam – File a complaint with the FTC and your state attorney general’s office documenting the scam parking text, fraudulent website and any financial harm done. Provide any details you have about the scam numbers, websites and messages.
Frequently Asked Questions About the “Unpaid Parking Invoice” Scam
1. How do I recognize this parking invoice scam text?
The scam text will claim to be from a city agency and state that your vehicle has an unpaid parking invoice. It provides a link to view and pay the invoice to avoid late fees. Be wary of any unsolicited texts regarding parking invoices, as legit notices are usually mailed. Watch for typos or incorrect URLs in the link.
2. What cities is this parking invoice scam text active in?
The scam has been reported in major cities like Los Angeles, New York, Chicago, Houston, Philadelphia, Phoenix, San Antonio, San Diego, Dallas, San Jose, Austin, Jacksonville, Fort Worth, Columbus, Charlotte, Indianapolis, San Francisco, Seattle, Denver, Washington DC, Boston, El Paso, Detroit, Nashville and others.
3. What information will the scam parking invoice website ask for?
The fake payment website will ask for your full name, birth date, address, phone number, email address, credit card number, expiration date and CVV code. This gives scammers enough to commit identity theft or access your accounts.
4. What do scammers do with my information if I fall for the scam?
Scammers use your personal and financial details to commit identity theft, make fraudulent charges to your accounts, take out loans/credit cards in your name, steal tax refunds, and more.
5. What steps should I take if I shared information through the scam website?
Immediately contact your credit card company to report fraudulent charges and cancel your card. Call your bank to monitor for suspicious transactions. Check your credit reports for signs of identity theft and consider a credit freeze. Change account passwords and enable two-factor authentication everywhere possible.
6. How can I avoid falling for the parking invoice scam?
Ignore unsolicited texts regarding parking invoices. Do not click on links or provide information to unfamiliar websites. Verify legitimacy with the city before paying anything online. Monitor financial statements routinely for fraudulent activity.
7. How do I report this scam parking invoice text?
File detailed complaints with the FTC, your state attorney general, and the police department in the city referenced in scam. Provide any website details, text message screenshots, and report any financial losses.
8. Are there legitimate reasons the city may text about parking invoices?
Very unlikely. Cities do not typically conduct official business via unsolicited text messages. Expect mailed invoices and verify directly with the city rather than trusting texts.
9. Can I get in trouble for ignoring these scam parking texts?
No, you cannot get in legitimate trouble with the city for ignoring scam texts regarding parking invoices. The texts are not from city agencies, even if made to look official.
10. Who should I contact if I’m unsure about a parking invoice text?
Reach out directly to your city’s parking authority via their official website to inquire about any outstanding invoices. Do not call phone numbers, click links or reply to the texts themselves.
The Bottom Line
In summary, be very wary of any text messages claiming your vehicle has an unpaid parking invoice. Do not click any links or provide personal or financial information to unfamiliar websites. These scam texts are on the rise in major cities, but a few simple precautions can help protect you:
- Ignore unsolicited texts regarding unpaid parking tickets or invoices. Legitimate notices are typically mailed to the registered vehicle owner.
- Never click on links in suspicious texts – type the URL directly into your browser. Watch for typos or slight variations.
- Don’t be rushed into providing sensitive information, even if threatened with late fees. Verify any payment website is legitimate first.
- Check statements routinely and report any unauthorized charges from this parking invoice scam immediately.
Staying alert to this scam can help you avoid serious financial damage from identity theft or fraudulent charges. Don’t let scammers fool you with official-looking logos and urgent pleas about unpaid invoices. Use caution and verify legitimacy before providing any personal or financial details.