- Apr 5, 2014
- 6,001
According to some Internet sources, it was reported that Trojan.Encoder.12544 penetrated an operating system using an update program of the application MEDoc, which is designed for taxation management. This encryption worm is also known as Petya, Petya.A, ExPetya and WannaCry-2. Doctor Web specialists have already encountered the similar distribution method of malicious programs before, and they know how to avoid such incidents in future.
Security researchers, who examined Trojan.Encoder.12544, inform that the original source of the Trojan was an update system of the program MEDoc. This program helps Ukrainian users in taxation management. The security researchers found that a tool named EzVit.exe, included in the MEDoc distribution kit and designed to update the main application, executed a CMD command at one point. This command launched the download of a malicious library. The main functionality of Trojan.Encoder.12544 was implemented in this library. Given that this encryption ransomware spreads via a network independently using a vulnerability in the SMB protocol and steals Windows user account data, further distribution of the infection is a matter of just one infected machine.
Back in 2012, Doctor Web security researchers detected a targeted attack on drugstores and pharmaceutical companies with the use of malicious program called BackDoor.Dande. This spyware Trojan stole information about a medication procurement from special programs used in the pharmaceutical industry. Once launched, the backdoor checked a system for presence of relevant applications for procurement and recording of purchase of medication and, if there weren’t any, it would shut down. More than 2800 drugstores and Russian pharmaceutical companies became victims of the infection. Thus, it is a fair assumption to say that BackDoor.Dande was used for business espionage.
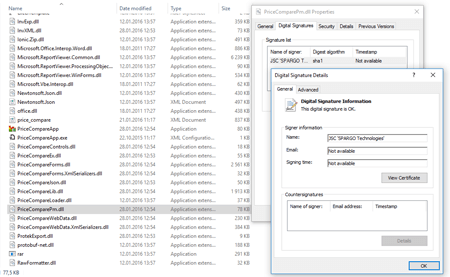
Doctor Web specialists have conducted an investigation that lasted as many as 4 years. One of the affected companies provided its hard drives compromised by BackDoor.Dande. Our analytics determined the creation date of a driver that launched all other backdoor components. This driver was mentioned in the Windows paging file and log of Avast anti-virus, which was installed on the infected machine. Analysis of these files showed that the malicious driver was created right after a launch of an application called ePrica (D:\ePrica\App\PriceCompareLoader.dll). This application was developed by a company called “Spargo Tekhnologii”. It allows executives of drugstores to analyze medication prices and to choose the best supplier. Examination of ePrica allowed to determine that it loads a library into the system. This library covertly downloads, decrypts and launches BackDoor.Dande. The Trojan was downloaded from IIS7. This website belonged to “Spargo Tekhnologii” and was designed to update ePrica. In addition, the module that covertly downloaded the malicious program had the valid digital signature “Spargo”. The Trojan loaded stolen data to servers located outside Russia. In other words, just as Trojan.Encoder.12544, the backdoor was “hidden” in the update module of the program.
Similarity of these cases shows that infrastructure of the software development requires a heightened level of awareness in terms of information security. To begin with, update process of any commercial software must be performed with a close attention of developers themselves and users. Some update tools of different programs have rights to install and launch executable files in an operating system. It can be an unexpected source of infection. In case of MEDoc, the infection was caused by the hack of cybercriminals and compromise of the update server. In the occasion of BackDoor.Dande, specialists assume that spread of infection was caused by deliberate actions of insiders. This method could be used by cybercriminals to conduct an effective aimed attack on users of practically any software.
Security researchers, who examined Trojan.Encoder.12544, inform that the original source of the Trojan was an update system of the program MEDoc. This program helps Ukrainian users in taxation management. The security researchers found that a tool named EzVit.exe, included in the MEDoc distribution kit and designed to update the main application, executed a CMD command at one point. This command launched the download of a malicious library. The main functionality of Trojan.Encoder.12544 was implemented in this library. Given that this encryption ransomware spreads via a network independently using a vulnerability in the SMB protocol and steals Windows user account data, further distribution of the infection is a matter of just one infected machine.
Back in 2012, Doctor Web security researchers detected a targeted attack on drugstores and pharmaceutical companies with the use of malicious program called BackDoor.Dande. This spyware Trojan stole information about a medication procurement from special programs used in the pharmaceutical industry. Once launched, the backdoor checked a system for presence of relevant applications for procurement and recording of purchase of medication and, if there weren’t any, it would shut down. More than 2800 drugstores and Russian pharmaceutical companies became victims of the infection. Thus, it is a fair assumption to say that BackDoor.Dande was used for business espionage.
Doctor Web specialists have conducted an investigation that lasted as many as 4 years. One of the affected companies provided its hard drives compromised by BackDoor.Dande. Our analytics determined the creation date of a driver that launched all other backdoor components. This driver was mentioned in the Windows paging file and log of Avast anti-virus, which was installed on the infected machine. Analysis of these files showed that the malicious driver was created right after a launch of an application called ePrica (D:\ePrica\App\PriceCompareLoader.dll). This application was developed by a company called “Spargo Tekhnologii”. It allows executives of drugstores to analyze medication prices and to choose the best supplier. Examination of ePrica allowed to determine that it loads a library into the system. This library covertly downloads, decrypts and launches BackDoor.Dande. The Trojan was downloaded from IIS7. This website belonged to “Spargo Tekhnologii” and was designed to update ePrica. In addition, the module that covertly downloaded the malicious program had the valid digital signature “Spargo”. The Trojan loaded stolen data to servers located outside Russia. In other words, just as Trojan.Encoder.12544, the backdoor was “hidden” in the update module of the program.
Similarity of these cases shows that infrastructure of the software development requires a heightened level of awareness in terms of information security. To begin with, update process of any commercial software must be performed with a close attention of developers themselves and users. Some update tools of different programs have rights to install and launch executable files in an operating system. It can be an unexpected source of infection. In case of MEDoc, the infection was caused by the hack of cybercriminals and compromise of the update server. In the occasion of BackDoor.Dande, specialists assume that spread of infection was caused by deliberate actions of insiders. This method could be used by cybercriminals to conduct an effective aimed attack on users of practically any software.