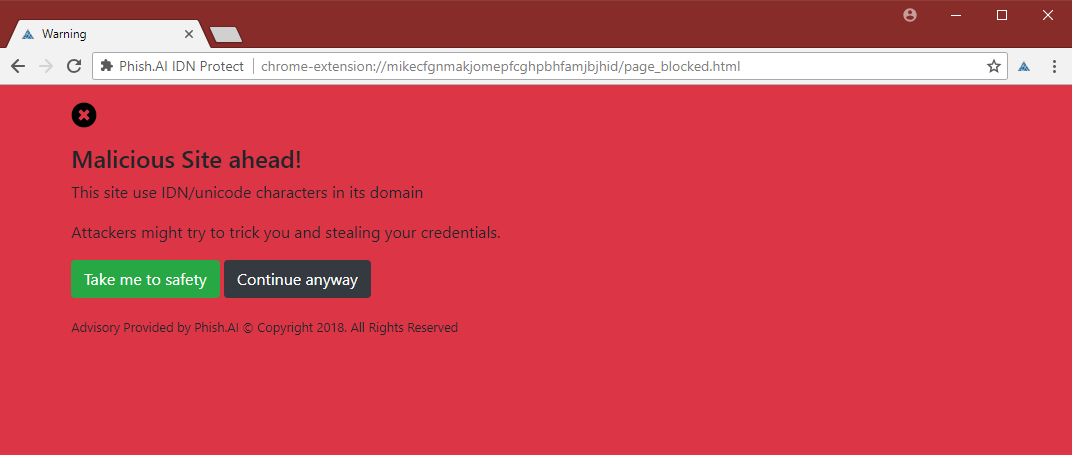
The team from Phish.ai has developed and released a Google Chrome extension that can detect when users are accessing domains spelled using non-standard Unicode characters and warn the users about the potential of a homograph attack.
Miscreants often use such intentionally misspelled domains to lure users on phishing sites, where they collect user credentials or trick victims into downloading files laced with malware.
How homograph attacks work
This is possible because more than a decade ago ICANN has allowed the registration of internationalized domain names, regionalized for various languages and alphabets, spelled using Unicode characters.
Some of these Unicode characters are
visually identical to standard Latin characters. This visual resemblance has opened the door for attackers to register domains that can fool users that don't pay close attention to the URL string.
For example, users must look very closely at coịnbạse.com to notice the small dots under the "i" and "a" characters.
Trying to trick users using such domains is called an internationalized domain name (IDN) homograph attack, or a Unicode attack. Such attacks have started becoming popular in recent years, with several incidents reported in the past year alone [1, 2, 3].