- Feb 4, 2016
- 2,520
After last week we had the KRACK and ROCA cryptographic attacks, this week has gotten off to a similarly "great" start with the publication of a new crypto attack known as DUHK (Don't Use Hard-coded Keys).
The issue at the heart of the DUHK attack is a combination of two main factors.
The first is the usage of the ANSI X9.31 Random Number Generator (RNG). This is an algorithm that takes random data and generates encryption keys used to secure VPN connections, browsing sessions, and other encrypted traffic/data.
The second factor needed for a DUHK attack is when hardware vendors use a hardcoded "seed key" for the ANSI X9.31 RNG algorithm. Normally, vendors should generate a random seed key at device startup or before launching the ANSI X9.31 algorithm.
This means that when you have hardware/software products that combine ANSI X9.31 and deploy a hardcoded seed key, attackers can decrypt encrypted communications carried out through that device. This includes communications passing over VPN connections or encrypted web sessions that carry out login credentials, payment information, Intranet information, private enterprise data, and more.
Old Fortinet FortiGate devices vulnerable to DUHK attacks
The DUHK attack was discovered by two researchers from the University of Pennsylvania and one researcher from Johns Hopkins University.
In a research paper they published today — entitled "Practical state recovery attacks against legacy RNG implementations" — researchers reveal they were able to recover encrypted traffic from Fortinet FortiGate devices used by companies across the world as firewalls or to create private VPN networks
DUHK attack takes up to 4 mins/connection
The attack is not trivial, but researchers say it's practical as an attacker using a modern computer can recover the encryption key in around four minutes per connection.
There is no user interaction needed to carry out a DUHK attack, as all the threat actor needs is a position to observe traffic coming from a vulnerable device. Because this is a passive network attack, victims cannot detect when someone uses a DUHK attack against them.
The research team also warns that other hardware and software products may also be affected by DUHK attacks. Researchers also published a list of products where they found hard-coded ANSI X9.31 seed keys.
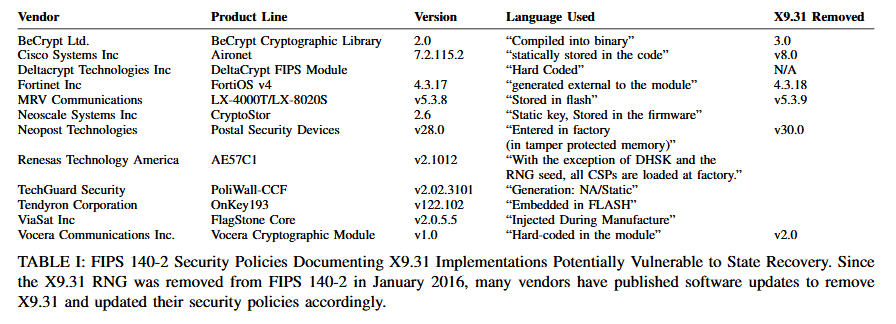
ANSI X9.31 was a very popular RNG algorithm
This is because ANSI X9.31 is very widespread. Up until January 2016, the algorithm was on the list of US government (FIPS) approved RNG algorithms.
ANSI X9.31 remained on the list until 2016, even if US NIST deprecated the algorithm in 2011, and scientists warned that the algorithm could be broken if the seed key ever leaked way back in 1998.
"If your product was certified after January 2016, then it is not vulnerable," the research team says. "If it was certified for the X9.31 RNG at any time, FIPS certification does not prevent this implementation vulnerability."
This is because vendors could have FIPS-compliant ANSI X9.31 implementations, but if they left a hard-coded seed key in the firmware, they automatically backdoored their own device's encryption.
More details about the DUHK attack are available on this dedicated homepage, and in a blog post by Matthew Green, one of the researchers.
