silversurfer
Super Moderator
Thread author
Verified
Top Poster
Staff Member
Malware Hunter
Forum Veteran
- Aug 17, 2014
- 12,737
- 123,876
- 8,399
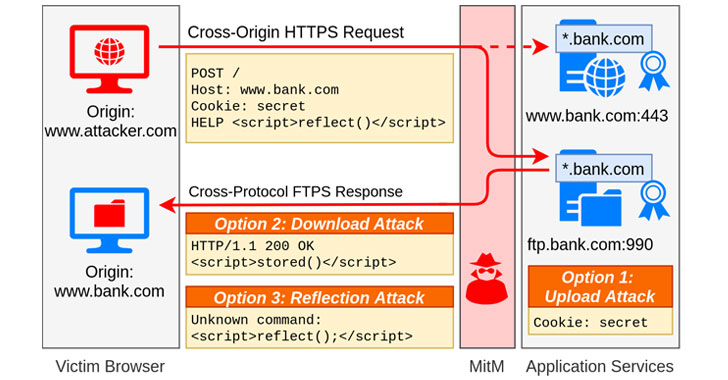
Researchers have disclosed a new type of attack that exploits misconfigurations in transport layer security (TLS) servers to redirect HTTPS traffic from a victim's web browser to a different TLS service endpoint located on another IP address to steal sensitive information.
The attacks have been dubbed ALPACA, short for "Application Layer Protocol Confusion - Analyzing and mitigating Cracks in tls Authentication," by a group of academics from Ruhr University Bochum, Münster University of Applied Sciences, and Paderborn University.
"Attackers can redirect traffic from one subdomain to another, resulting in a valid TLS session," the study said. "This breaks the authentication of TLS and cross-protocol attacks may be possible where the behavior of one protocol service may compromise the other at the application layer."
TLS is a cryptographic protocol underpinning several application layer protocols like HTTPS, SMTP, IMAP, POP3, and FTP to secure communications over a network with the goal of adding a layer of authentication and preserving integrity of exchanged data while in transit.
ALPACA attacks are possible because TLS does not bind a TCP connection to the intended application layer protocol, the researchers elaborated. The failure of TLS to protect the integrity of the TCP connection could therefore be abused to "redirect TLS traffic for the intended TLS service endpoint and protocol to another, substitute TLS service endpoint and protocol."

New TLS Attack Lets Attackers Launch Cross-Protocol Attacks Against Secure Sites
ALPACA Attack: A new TLS attack allows attackers to launch cross-protocol attacks against secure sites.
 thehackernews.com
thehackernews.com