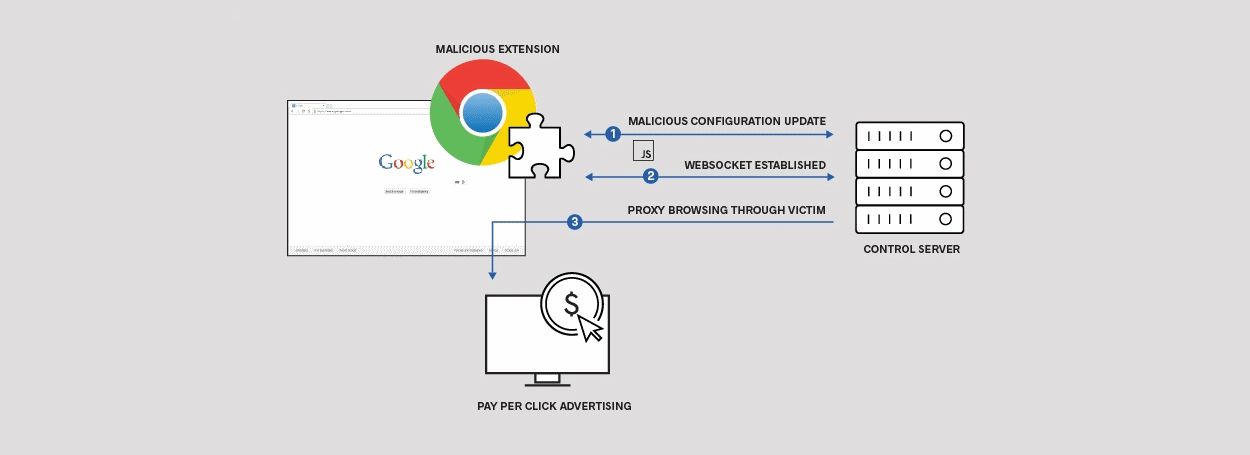
Security researchers from US cyber-security firm ICEBRG have spotted four Chrome extensions featuring malicious code that were available through the official Chrome Web Store.
According to researchers, the four Chrome extensions were designed to allow attackers to send malicious commands to users' browsers in the form of JavaScript code, but attackers only used this ability to perform click fraud by loading a site in the background and clicking on ads.
The names of the four extensions are Change HTTP Request Header (ppmibgfeefcglejjlpeihfdimbkfbbnm), Nyoogle - Custom Logo for Google (ginfoagmgomhccdaclfbbbhfjgmphkph), Lite Bookmarks (mpneoicaochhlckfkackiigepakdgapj), and Stickies - Chrome's Post-it Notes (djffibmpaakodnbmcdemmmjmeolcmbae).
Of the four, Nyoogle is still available on the Chrome Web Store at the time of writing.
In total, over 500,000 users were using the extensions when ICEBRG detected the malicious behavior and notified the National Cyber Security Centre of The Netherlands (NCSC-NL), the United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team (US-CERT), and the Google Safe Browsing Operations team.
While three of the four extensions were removed from the Chrome Web Store, many users still have the extensions loaded in their browsers.
The company has published a detailed report on the extensions' malicious behavior in the hopes that users will take the time to check their browser and remove the malicious extensions for their computers.
It is unclear if the same group is behind all four extensions, but ICEBRG said the four extensions featured similar tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).