Has your inbox been bombarded by urgent emails claiming you have a Bitcoin payment waiting for you on Coinbase? Don’t let your emotions get the best of you – this “You Have 1 New Transaction” scam is after your money and personal information.
This phishing scheme uses clever social engineering and fake notifications to convince you to hand over login credentials or sensitive financial details. Don’t let them swindle you out of your hard-earned crypto assets.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll outline exactly how this scam works step-by-step and provide actionable tips to avoid getting hooked by the bait. Read on to uncover their tricks so you can protect your accounts and cryptocurrency wallets.
Scam Overview: Anatomy of the “You Have 1 New Transaction” Coinbase Phishing Attack
The “You Have 1 New Transaction” scam is a prime example of a phishing attempt. Phishing employs social engineering techniques to trick users into handing over sensitive information and money.
This particular phishing scam starts with an email designed to look like legitimate Coinbase correspondence. The email claims that a Bitcoin payment is waiting to be claimed on your account from another source, like Binance.
Urgency is created by saying there is a short 24-48 hour timeframe before the transaction expires. These emails often include:
- Coinbase branding and logo
- A BTC amount ready for payout
- Fake transaction hashes and details
- A countdown timer
- A “Complete Payout” or “Get Bitcoin” button
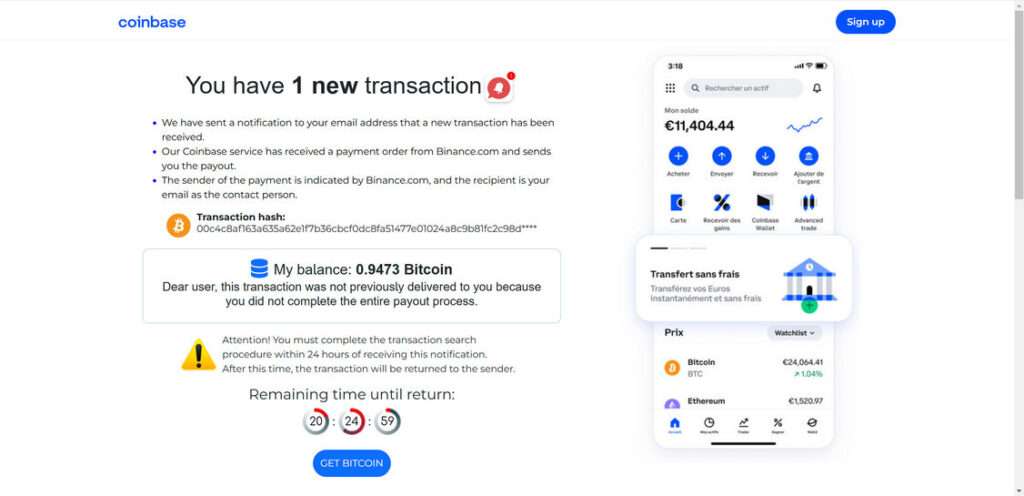
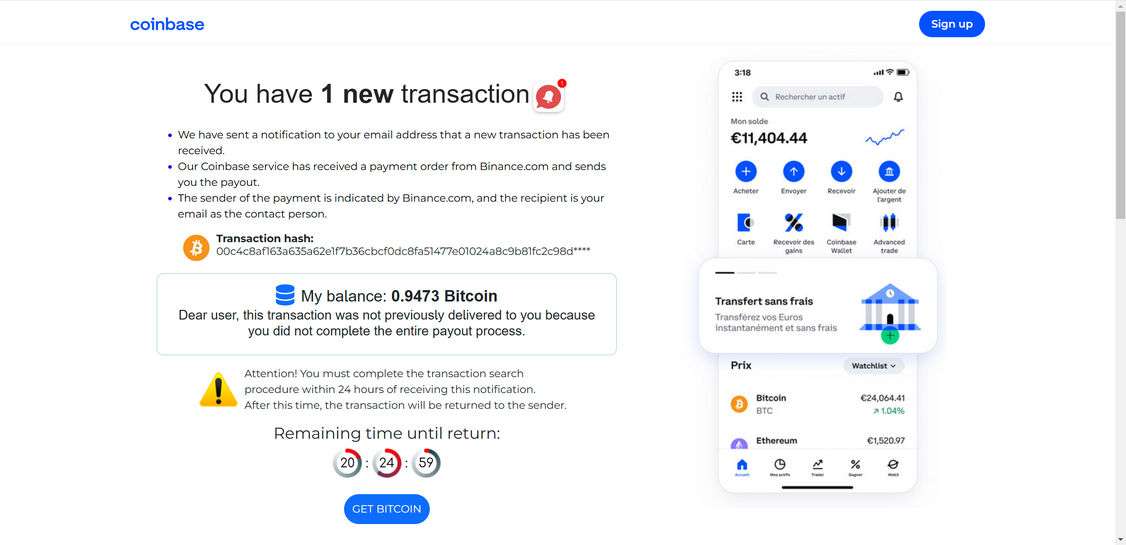
Here is how the scam emai might look:
You have 1 new transaction
We have sent a notification to your email address that a new transaction has been received.
Our Coinbase service has received a payment order from Binance.com and sends you the payout.
The sender of the payment is indicated by Binance.com, and the recipient is your email as the contact person.
Transaction hash:
00c4c8af163a635a62e1f7b36cbcf0dc8fa51477e01024a8c9b81fc2c98d****
My balance: 0.9473 Bitcoin
Dear user, this transaction was not previously delivered to you because you did not complete the entire payout process.
Attention! You must complete the transaction search procedure within 24 hours of receiving this notification.
After this time, the transaction will be returned to the sender.
If the recipient clicks through, they are taken to a convincing fake Coinbase site. The site prompts the user to enter personal details like name, email, and Coinbase login credentials to “complete the payout”.
In other cases, it may ask for payment information like a credit card or Bitcoin wallet address, along with a service fee, to release the funds.
Once submitted, the scammers have what they’re after: your sensitive information. The fake sites are set up to steal login credentials, passwords, identity information, and money from trusting individuals.
How the “You Have 1 New Transaction” Scam Works
Now that we’ve outlined the basic scam structure, let’s break it down step-by-step:
Step 1: You Receive an Email
The scam starts with an email crafted to look like it’s from Coinbase. The sender name, email address, logo, and colors mimic the real Coinbase brand.
The email copy explains that Coinbase has received a BTC payment headed to your account. It claims to be from another company, like Binance, and contains fake transaction hashes and details.
Urgency is created with a short 24-48 hour timeframe before the transaction will supposedly expire or be reversed. This pushes the recipient to act quickly.
Step 2: Click the Call-To-Action
The email includes a call-to-action button or link, like “Complete Payout Delivery” or “Claim Bitcoin”. This button is designed to bring you to the fake phishing site.
Some emails ask the recipient to login to Coinbase to find the pending transaction, then contact an included customer support email or number for help “completing the transfer”. This support channel is controlled by the scammers.
Step 3: Enter Your Information
After clicking the call-to-action, you are brought to a false Coinbase website. The site has the Coinbase aesthetic and domain, but is hosted on an alternate server.
You are prompted to enter personal details like your name, email address, and Coinbase credentials to “complete the transaction”. In other variants, it may ask for payment details and a release fee.
Step 4: The Site Steals Your Data
Once submitted, your sensitive personal information is harvested by the scammers. The site is designed to capture and send login credentials, identity details, credit card numbers, and other data points.
In some cases, if bitcoin wallet or credit card information is provided, the scammers may also immediately steal funds.
Step 5: Criminals Access Your Accounts
With your username and password in hand, the attackers will attempt to access your real Coinbase account and any other linked sites. They can drain cryptocurrency wallets, steal identities, and commit payment fraud.
The criminals can also sell account details on the dark web to other bad actors. This exposes you to future attacks by expanding the reach of the stolen data.
This is how a standard “You Have 1 New Transaction” phishing attempt plays out and puts user assets at risk. Being aware of each step can help identify and avoid the scam. Next, we’ll outline some warning signs to watch for.
5 Red Flags to Spot the Coinbase “You Have 1 New Transaction” Scam
While scammers are becoming more convincing, there are still telltale signs that reveal their phishing attempts. Be on high alert for these red flags:
1. Generic Greetings
Legitimate emails from companies will address you directly by name. Phishing emails often start with impersonal greetings like “Dear user” to cast a wide net.
2. Suspicious Sender Address
Check that the sender email address matches the company’s real domain, like support@coinbase.com. Scam emails will show odd email addresses when inspected closer.
3. Spelling/Grammar Errors
Sloppy spelling and sentence structure is a giveaway. Real corporations thoroughly proofread communications.
4. Requests Sensitive Information
Coinbase and banks will never ask for your password, social security number, or account numbers over email. If an email requires sensitive details upfront, it’s likely a scam.
5. Urgent Deadline
Being rushed to act by an impending deadline is a common tactic scammers use to prey on fear and urgency. It’s best to pause and verify any time-sensitive demands.
Learning to recognize these types of warning signs will help identify and block phishing attempts before they succeed.
What To Do If You Fall Victim to the Coinbase “You Have 1 New Transaction” Scam
If you entered personal information or sent money to a “You Have 1 New Transaction” scam, stay calm but act swiftly to contain the damage. Here are 5 essential next steps:
1. Contact Coinbase Support
If you provided account login details, immediately reach out to Coinbase support. They can lock down your account and assess any unwanted access or activity.
2. Reset Passwords
For any sites or accounts that may have had compromised credentials entered, reset passwords and enable two-factor authentication for increased security.
3. Watch for Unauthorized Activity
Closely monitor financial accounts for any signs of fraudulent access or transactions. Report any unauthorized activity to your bank or payment provider.
4. Place Fraud Alert
Consider placing a fraud alert with credit bureaus to signal that your identity may be compromised. This makes it harder for criminals to open new accounts in your name.
5. File Police Reports
If funds were stolen, file reports with local law enforcement and the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center. Provide any relevant email headers, transaction details, and scam site screenshots to aid investigation.
While falling victim to a scam can be scary, taking proactive measures swiftly can help limit damages and regain security.
Frequently Asked Questions: How to Identify and Avoid the Coinbase “You Have 1 New Transaction” Scam
1. What is the “You Have 1 New Transaction” scam?
The “You Have 1 New Transaction” scam is a phishing attack targeting Coinbase users. Scammers send fake emails pretending to be from Coinbase, stating that a Bitcoin payment is waiting to be claimed. The email prompts victims to click a link bringing them to a fake Coinbase login page to “complete the transfer”. If users enter their username and password, the criminals gain account access and can steal funds.
2. How do I recognize a fake “You Have 1 New Transaction” email?
Warning signs include poorly worded or generic greetings, unusual sender addresses, spelling/grammar errors, and demands for sensitive information. Real Coinbase emails address you by name, come from @coinbase.com addresses, are professionally written, and never ask for your password or account numbers.
3. What information do scammers gain through this phishing scam?
The scammers aim to harvest login credentials, personal information, credit card numbers, and any other sensitive details entered on the fake Coinbase site. With account access, they can drain cryptocurrency wallets and steal identities.
4. What should I do if I entered my information into a “You Have 1 New Transaction” scam site?
If you provided any account details, immediately contact Coinbase support to lock down your account. Reset any compromised passwords and enable two-factor authentication. Watch for unauthorized transactions and report any that occur. Place fraud alerts and file police reports if necessary.
5. How do I secure my Coinbase account from phishing scams?
Use unique complex passwords, enable two-factor authentication, bookmark the real Coinbase URL, check sender addresses on emails, ignore demands for information through emails/texts, and always verify requests through official customer support.
6. Can I get back stolen funds from this scam?
Unfortunately, recovering stolen cryptocurrency can be very challenging, if not impossible. This is why it’s critical to take preventative measures and avoid falling victim to scams in the first place through education and vigilance.
7. How can I report a “You Have 1 New Transaction” phishing attempt or site?
Forward scam emails to phish@coinbase.com. Report fake sites to Coinbase security and the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center. Notify other exchanges like Binance if their branding is misused. The more reports filed, the better chance there is to halt these scams.
8. How widespread is this Coinbase phishing scam?
The “You Have 1 New Transaction” scam has been heavily circulating since around 2020, targeting millions of Coinbase users worldwide. Cybercriminals modify their tactics but rely on social engineering to exploit human emotions of fear, curiosity, urgency, and greed.
9. How can I stay on top of new phishing scams targeting Coinbase users?
Follow official Coinbase social media and blog updates for security alerts. Report scams to help warn others. Stay involved in cryptocurrency forums and communities to stay vigilant about new threats as they arise. Education is the best prevention.
10. What proactive steps can I take to improve my crypto security?
Use unique complex passwords, enable two-factor authentication on exchanges, use a password manager, download antivirus software, educate yourself on phishing techniques, bookmark official sites, and never share sensitive account details unless you initiate contact. Being cautious and prepared is your best defense.
The Bottom Line: How to Stay Safe from the Coinbase “New Transaction” Scam
In summary, the Coinbase “You Have 1 New Transaction” phishing scam is a dangerous threat targeting account information and money. But there are key steps cryptocurrency holders can take to identify scams and protect assets:
- Never click links or download attachments from unsolicited emails, no matter how realistic they appear. Manually navigate to sites using a verified bookmark.
- Double check sender emails and domains for accuracy. Be wary of typos, misspellings, or non-official addresses.
- Use unique, complex passwords for each account. Enable two-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Do not provide personal, login, or payment information through emails or texts. Legitimate companies will never request sensitive details this way.
- Watch for urgent deadlines, negative consequences for inaction, and threatening language. These are manipulation tactics.
- When in doubt, directly contact customer support through the official website to verify unusual requests.
- Report scam attempts to notify companies and regulators working to protect consumers.
By recognizing the hallmarks of phishing scams, enacting security best practices, and acting cautiously online, cryptocurrency holders can keep assets secure against even sophisticated attacks. Stay vigilant about scams targeting the crypto community as adoption grows.
Spreading awareness about the tactics and mechanics of scams like the fake Coinbase email can help users across the blockchain ecosystem protect themselves and their funds. Keep the conversation going across social channels and forums to empower the community with knowledge.

![Remove AudioSearchPro.com Redirect [Virus Removal Guide] 6 audiosearchpro.com scam 1](https://malwaretips.com/blogs/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/audiosearchpro.com-scam-1-290x290.jpg)
![Remove Cosmobotshield.co.in Pop-up Ads [Virus Removal Guide] 8 McAfee scam 4](https://malwaretips.com/blogs/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/McAfee-scam-4-290x290.jpg)
