L
LabZero
Thread author
The redirect to malicious pages because of DNS hijacking seems to occur on devices connected to the same local network (desktop, laptop, smartphone, tablet,...), in spite of the antimalware does not detect the presence of any infection.
The redirection happens on all of those devices where it has not been manually configured to use specific DNS servers, and then specifically request the router the addresses of the DNS you want to use (assignment via DHCP).
In short, the criminals change the DNS on the router by replacing the ones manually set by us (or received from the ISP) with malicious DNS containing altered records.
Suppose that the router had previously been set to Google DNS server (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) as in my case, and assume that these DNS resolving, for example, the mnemonic adress for Yahoo with IP 46.228.47.115
To ensure it, you can type in Windows command prompt:
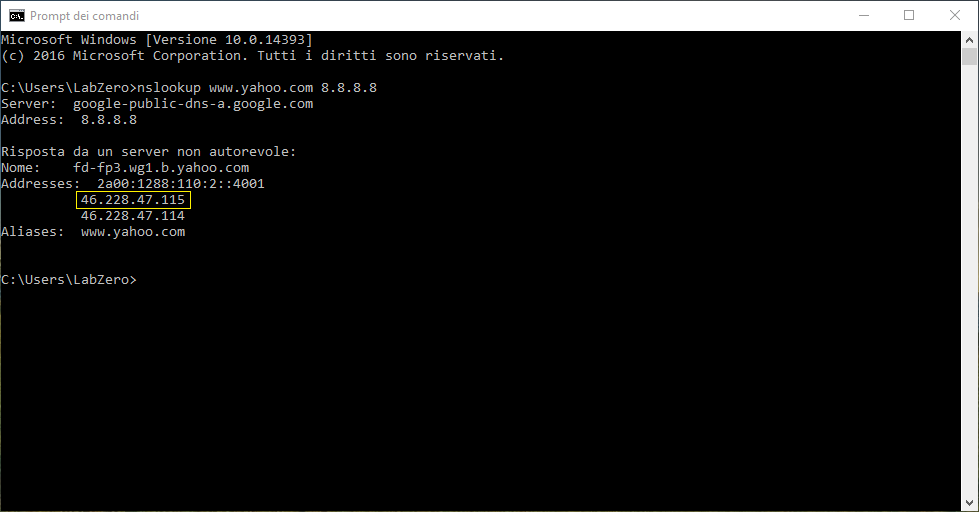
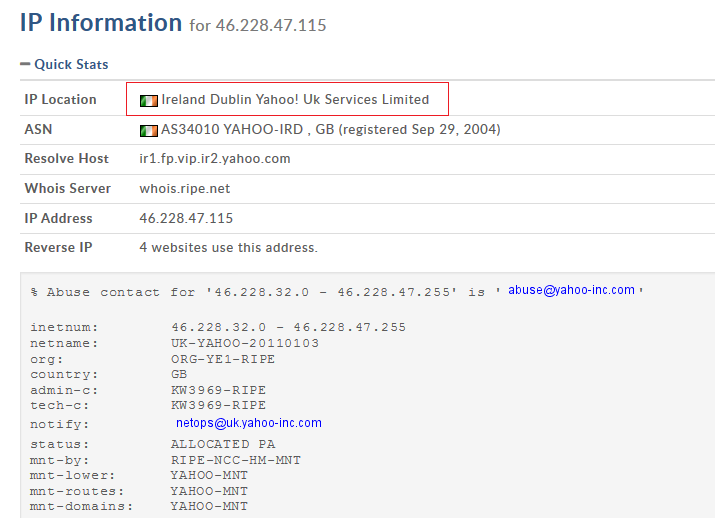
By entering the IP 46.228.47.115 here http://whois.domaintools.com/ we will notice immediately that it is a IP of Yahoo (all correct!).
Then : http://whois.domaintools.com/46.228.47.115
The DNS server changed on the router by criminals, probably will not solve www.yahoo.com as IP 46.228.47.115
but with an arbitrary IP, which typically refers to a malicious page.
It will be easy to verify it by typing, at the command prompt, as follows:
In place of IP MALICIOUS DNS will have to be obviously specified the IP of the DNS that you might find in the configuration panel of the router instead of the address previously set.
By inserting the malicious IP in the website mentioned above, you realize that it is not Yahoo.
Solve the problem of DNS changed on the router
To delete the DNS changed on the router by fixing the problem, you can follow these simple steps:
1) Perform, from one device connected to the router in the local network, this test rom-0 test
It is a check on the assignment of domain names.
The web page can detect the IP address that in 99% of the cases (except that you have to use applications for the masking of IP) is the address assigned by the ISP to your router, at the time of the connection.
By clicking on the Test button, then, it is immediately possible to establish if your device is less vulnerable to attacks coming from the outside.
2) Access the configuration interface of the router.
In the case in which the default password and username (usually admin,admin or admin,password) not changed by you, do not work anymore, then it is highly likely that, in addition to having modified the DNS server, the attackers have also altered the default username and password. In this case, you will need to do a full reset of the router (using the "hidden" button generally located on the back of the device).
Then make a new router configuration from scratch and assign custom and strong new password.
3) Check the DNS server on the router.
The section of the configuration panel of the router where you can set the addresses of the DNS servers to use, change from manufacturer to manufacturer and from model to model.
Usually, however, the adjustments related to the DNS server are in the sections Interface settings, Network settings, WAN/LAN settings.etc
The redirection happens on all of those devices where it has not been manually configured to use specific DNS servers, and then specifically request the router the addresses of the DNS you want to use (assignment via DHCP).
In short, the criminals change the DNS on the router by replacing the ones manually set by us (or received from the ISP) with malicious DNS containing altered records.
Suppose that the router had previously been set to Google DNS server (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) as in my case, and assume that these DNS resolving, for example, the mnemonic adress for Yahoo with IP 46.228.47.115
To ensure it, you can type in Windows command prompt:
Code:
nslookup www.yahoo.com 8.8.8.8By entering the IP 46.228.47.115 here http://whois.domaintools.com/ we will notice immediately that it is a IP of Yahoo (all correct!).
Then : http://whois.domaintools.com/46.228.47.115
The DNS server changed on the router by criminals, probably will not solve www.yahoo.com as IP 46.228.47.115
but with an arbitrary IP, which typically refers to a malicious page.
It will be easy to verify it by typing, at the command prompt, as follows:
Code:
nslookup www.yahoo.com IP MALICIOUS DNSIn place of IP MALICIOUS DNS will have to be obviously specified the IP of the DNS that you might find in the configuration panel of the router instead of the address previously set.
By inserting the malicious IP in the website mentioned above, you realize that it is not Yahoo.
Solve the problem of DNS changed on the router
To delete the DNS changed on the router by fixing the problem, you can follow these simple steps:
1) Perform, from one device connected to the router in the local network, this test rom-0 test
It is a check on the assignment of domain names.
The web page can detect the IP address that in 99% of the cases (except that you have to use applications for the masking of IP) is the address assigned by the ISP to your router, at the time of the connection.
By clicking on the Test button, then, it is immediately possible to establish if your device is less vulnerable to attacks coming from the outside.
2) Access the configuration interface of the router.
In the case in which the default password and username (usually admin,admin or admin,password) not changed by you, do not work anymore, then it is highly likely that, in addition to having modified the DNS server, the attackers have also altered the default username and password. In this case, you will need to do a full reset of the router (using the "hidden" button generally located on the back of the device).
Then make a new router configuration from scratch and assign custom and strong new password.
3) Check the DNS server on the router.
The section of the configuration panel of the router where you can set the addresses of the DNS servers to use, change from manufacturer to manufacturer and from model to model.
Usually, however, the adjustments related to the DNS server are in the sections Interface settings, Network settings, WAN/LAN settings.etc
Last edited by a moderator:
