A new scam is circulating in the crypto world, targeting Ethereum users who have paid high gas fees over the years. Promising refunds in the form of a token called $gETH, this scheme looks polished and even claims endorsement from the Ethereum Foundation and co-founder Vitalik Buterin. But it’s a fraud—designed to empty your wallet.
Here’s everything you need to know about this scam, how it works, how to protect yourself, and what to do if you’ve already fallen victim.

Scam Overview: What Is the $gETH “ETH Gas Fees Refund” Scam?
The $gETH token scam is a sophisticated phishing attack disguised as a reward program. The premise sounds appealing: Ethereum users who’ve historically spent ETH on gas fees are now supposedly eligible for a refund via a new token called $gETH, allegedly issued by the Ethereum Foundation. The fake token is presented as a compensation mechanism linked to the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade.
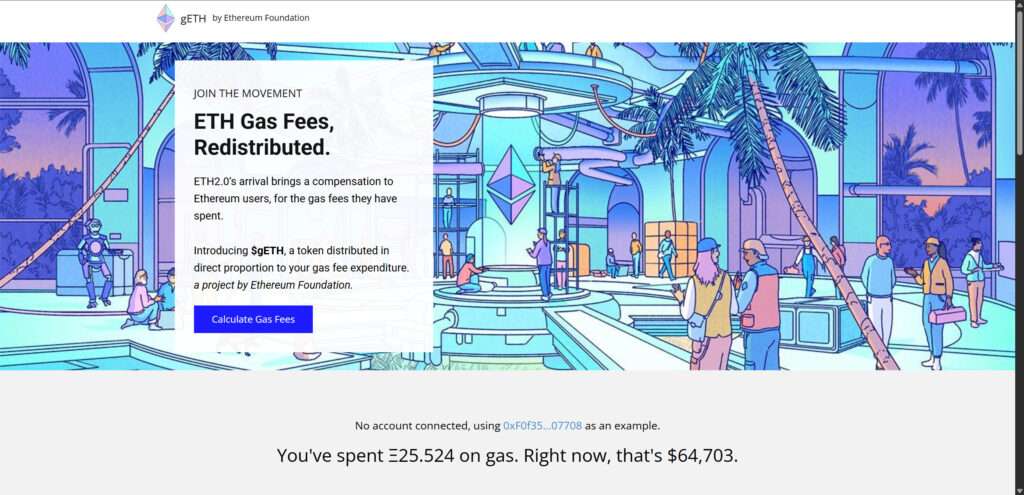
The scam’s website is slick. It displays Ethereum branding, uses the name and image of Vitalik Buterin, and claims the token is being distributed to recognize those who spent significant gas fees before Ethereum 2.0’s rollout.
Here’s what the scam claims:
- $gETH is a new token developed by the Ethereum Foundation
- It will be used as the main gas token in the new ETH 2.0 ecosystem
- The token will be distributed proportionally based on your historical gas usage
- You can claim thousands of dollars in $gETH after calculating your total gas fee expenditure
- All you need to do is connect your wallet and sign a transaction
In reality, none of this is true. Ethereum Foundation has made no such announcement, and Vitalik Buterin has never endorsed a $gETH token. The scam exploits legitimate Ethereum terminology and issues—gas fees, ETH 2.0 upgrades, sharding, validator incentives—to make its story sound credible.
The fake site typically calculates how much you’ve supposedly spent on gas and how much $gETH you can claim. It may tell you you’ve spent something like 25 ETH on gas and are owed $12,000 in refunds. The numbers are designed to convince you of the reward’s authenticity and get you to proceed with the next step: connecting your wallet.
Once you do that, the scam reaches its critical phase—stealing your crypto assets.
How the Scam Works
Understanding how the $gETH scam operates is key to avoiding it. Here’s how it typically unfolds.
Step 1: The Setup
The scammers run social media ads, post on Reddit, Discord, Telegram, and sometimes even comment on real Ethereum-related threads. These posts often include:
- Links to professional-looking sites
- Statements like “ETH2.0 is here—claim your gas fee refund”
- Promises of thousands in ETH for historical gas use
These platforms often include sites hosted on domains like gas.zip, gethrefund.xyz, or ethgasclaim.site. The names change frequently to bypass spam filters and domain blacklists.
Step 2: The Fake Ethereum Website
Once on the site, users see a clean, professional-looking page with the Ethereum logo, a headshot of Vitalik Buterin, and calls to action like “Join the Movement” or “Time to Gas Fee Refunds.”
The site often includes a fake gas calculator. It may show:
- Total ETH you spent on gas
- Number of transactions
- Average Gwei cost
- Your eligibility amount in $gETH (e.g., $14,783.50)
This is a psychological play to convince users that the offer is real and personalized based on blockchain data. In truth, the data is often faked or roughly estimated using public wallet information.
Step 3: Wallet Connection
To claim your refund, the site prompts you to connect your wallet using MetaMask, WalletConnect, or another Web3-compatible wallet. This interaction appears harmless at first.
However, the real danger begins when you’re asked to sign a transaction.
Step 4: Signing a Malicious Contract
You are asked to “authorize,” “claim,” or “sign” a transaction. This is not a simple signature. Instead, it is often an authorization for the attacker to manage your tokens.
The signed transaction typically uses malicious smart contract functions like:
setApprovalForAll(used to access NFTs)approve()(to control ERC-20 tokens)permit()(a newer function that enables gasless approvals)
These functions give the scammer control over your assets. Some users may not notice anything unusual at this stage because no ETH is requested or visibly sent.
Step 5: Wallet Drain
Once the attacker has access, the wallet is drained in seconds. ERC-20 tokens, NFTs, and other assets are transferred out to attacker-controlled wallets. Transactions are automated, using bots or scripts that listen for approvals and act instantly.
Step 6: Cover-Up and Exit
After executing the scam:
- The site is often taken down or relocated
- The domain is abandoned or redirected to a different scam
- Social media ads disappear or are rebranded
- The stolen funds are routed through mixers or converted via decentralized exchanges
Because everything happens on-chain, there’s no recourse to reverse the transactions. Victims are left without assets and with no direct path to recovery.
What to Do if You Have Fallen Victim to This Scam
If you’ve interacted with the scam site or signed any transactions, here’s what you need to do immediately.
1. Disconnect Your Wallet
Go to your wallet (e.g., MetaMask) and disconnect from all connected sites. This alone won’t remove contract permissions, but it will prevent further interactions.
2. Revoke Token Approvals
Use one of the following tools:
Paste your wallet address, review contract approvals, and revoke any that look suspicious. This step is critical to prevent the attacker from continuing to drain your wallet.
3. Transfer Remaining Assets to a New Wallet
Create a new wallet using a clean device. Transfer all remaining tokens, NFTs, and ETH to the new wallet. Do not use the compromised wallet again.
4. Report the Scam
Help protect others by reporting the scam to:
- Chainabuse
- MetaMask Support
- Twitter (if the scam was advertised there)
- Discord or Telegram communities
Include any links, screenshots, or wallet addresses associated with the scam.
5. Monitor Wallet Activity
Set up alerts using:
These tools allow you to track transactions involving your address or contracts associated with it.
6. Educate Your Network
Share your experience. Post a warning on social media, Reddit, or Discord. Warn others in NFT or Ethereum-focused groups to prevent future victims.
7. Run Security Checks on Your Device
Scan your device for malware. Uninstall any suspicious browser extensions. Ensure your device hasn’t been compromised by keyloggers or phishing tools.
Why This Scam Is So Effective
The $gETH scam works because it preys on:
- Real frustrations with Ethereum gas fees
- Real news about Ethereum 2.0 upgrades
- Real figures and buzzwords from the Ethereum ecosystem
- User trust in the Ethereum Foundation and Vitalik Buterin
- A lack of technical understanding about smart contract permissions
This is why it’s critical to verify everything—even if it seems like it’s coming from a trusted source.
How to Avoid Similar Scams in the Future
Stay safe with these simple rules:
- Never sign a contract or transaction you don’t fully understand
- Always double-check domain names and look for subtle typos
- Verify announcements via official Ethereum channels or Vitalik’s verified profiles
- Use tools like WalletGuard or ScamSniffer browser extensions to detect phishing sites
- Be skeptical of offers that seem too good to be true, especially ones that promise free money or rewards
If you’re ever unsure, don’t act impulsively. Ask trusted crypto communities before connecting your wallet to any site.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About the $gETH Scam
What is the $gETH token scam?
The $gETH scam is a fake Ethereum-based airdrop that falsely claims to refund gas fees to users in the form of a new token called $gETH (gasETH). It pretends to be an initiative by the Ethereum Foundation to redistribute gas fees following the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. In reality, it is a phishing scheme designed to trick users into connecting their wallets and signing malicious contracts that allow scammers to steal their crypto assets.
Is $gETH a real Ethereum token?
No, $gETH is not a legitimate Ethereum token. There has been no official announcement from the Ethereum Foundation or Vitalik Buterin regarding such a token. Any site or project claiming that $gETH is an official Ethereum refund mechanism is a scam.
How does the $gETH scam work?
The scam operates by:
- Luring users through fake social media posts or ads.
- Redirecting them to a fake Ethereum-branded website.
- Displaying a fake “gas fee calculator” showing how much ETH they’ve spent on gas.
- Offering a large refund in $gETH tokens.
- Prompting users to connect their wallet.
- Requiring them to sign a smart contract that secretly gives scammers access to their assets.
What happens if I connect my wallet to the scam site?
If you connect your wallet but do not sign any transactions, your funds are likely still safe. However, the site may try to trick you into signing a malicious contract. Once you sign it, you may unknowingly give the scammers permission to move your tokens, NFTs, or ETH out of your wallet.
What should I do if I interacted with the scam?
Take these steps immediately:
- Disconnect your wallet from the scam site via your wallet app.
- Use a tool like Revoke.cash to remove all smart contract approvals.
- Transfer any remaining assets to a new wallet.
- Report the scam to relevant platforms and authorities.
- Monitor your wallet using tools like Tenderly or Zapper for suspicious activity.
Can I get my money or tokens back?
Unfortunately, no. Once funds are stolen through a signed smart contract on the blockchain, the transactions are irreversible. There are no chargebacks in crypto. However, you can help others by reporting the scam and spreading awareness.
How can I tell if a crypto project or airdrop is a scam?
Here are a few red flags:
- It promises large rewards for little to no effort.
- It asks you to urgently sign a contract or connect your wallet.
- It uses language that mimics legitimate Ethereum updates without official confirmation.
- The domain looks suspicious or slightly misspelled (e.g., ethrefunds.xyz instead of ethereum.org).
- There’s no verifiable announcement from Ethereum’s official channels.
Is this scam related to Ethereum 2.0?
No, it’s not. The Ethereum Foundation has not issued any refund token or compensation mechanism related to Ethereum 2.0. Scammers are simply using the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade as a hook to make their scheme sound believable.
Where can I report the scam?
You can report the scam through:
- Chainabuse.com
- MetaMask’s phishing form
- Twitter or X (report the post/ad)
- Reddit, Discord, and Telegram groups you’re part of
- ScamSniffer or PhishFort if you use browser extensions that collect phishing data
How can I protect myself from future crypto scams?
- Always verify projects through official channels like ethereum.org, Vitalik’s verified accounts, or GitHub repositories.
- Don’t connect your wallet to unknown or unverified sites.
- Use browser extensions that detect phishing attempts.
- Regularly check and revoke token approvals.
- Educate yourself about how smart contracts and signatures work.
The Bottom Line
The $gETH token scam is a sophisticated phishing attack that takes advantage of the Ethereum community’s knowledge of gas fees and anticipation around ETH 2.0. By presenting a polished, official-looking site and offering fake rewards, scammers are stealing millions in crypto assets from unsuspecting users.
If you’ve been targeted, take immediate steps to revoke access, move your assets, and report the scam. And for everyone else, remember: in crypto, security is your responsibility. Stay vigilant, verify everything, and trust only what you can independently confirm.



