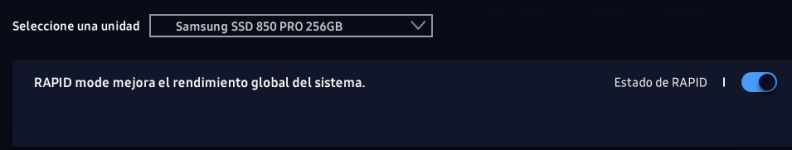
What is RAPID Mode Technology
RAPID mode is paired exclusively with Samsung SATA SSDs (840 series and above) and available as a feature of the accompanying Samsung SSD Magician Software Toolset (version 4.2 and later). When configured correctly, RAPID mode functions as a filter driver within the Windows storage stack. The filter driver continuously monitors all storage-related activity between the Operating System (OS), user applications and the SSD. RAPID mode analyzes all system traffic, leveraging extra system resources such as DRAM/CPU to dynamically provide read acceleration via intelligent caching of "hot data" and write optimization.
The concept behind RAPID mode: Your computer "learns" from your computer habits. It recognizes frequently launched applications and attempts to make them instantly available when you first login to your system. Helping applications, databases, webpages, and general use functions to launch quickly due to high usage.
Hot Data
Read acceleration technology in RAPID mode leverages spare system DRAM and CPU resources to manage a change in "hot data". As your system stores hot data in memory, system performance is improved as similar requests for that data are performed; then, data is served directly from DRAM rather than the system having to pull from a storage device. Latency, throughput and overall daily user experience for the most active data are improved. Taking a simple approach to caching the most recently accessed data, RAPID mode operates almost as an extension of the OS cache. RAPID mode handles not just new data, but very carefully takes into account frequency of access, file types, system status, RAM availability, etc. RAPID mode may exclude certain data from the cache based on a variety of factors by excluding certain data not regularly used. This prevents unnecessary data from polluting the cache and allows us to keep the memory footprint to a minimum. Files that RAPID mode deems meaningless to cache (such as large media files) are dismissed.
Hot data is cumulative and persistent across multiple sessions and reboots so that if you have been working on a specific file or application you will be able to access critical data faster as well.
Impervious Performance
A consistent performance bottleneck users experience is usually caused by background tasks performed by the OS such as updating, logging, or indexing. When your PC stutters, it is often caused by these small random transactions frequently failing to complete in a timely manner. RAPID mode favors transactions that can be processed in parallel thereby dramatically improving the completion time for these small transactions. This almost entirely eliminates any storage-related stuttering and can be hugely beneficial to some aspects of system performance.