- Aug 17, 2014
- 11,775
" Extensions installed in web browsers may be used for tracking purposes. Some extensions use resources that are accessible by sites that are loaded in the browser; the information may be used to determine if extensions are installed, and even which extensions. "
Fingerprinting describes a series of tracking techniques that Internet sites and apps may use to track users. The techniques use information, either provided automatically by the browser or the operating system, or manually, through the use of scripts. Unique fingerprints are the goal, as they allow sites to distinguish between visitors accurately. Most of the time, fingerprinting is used in combination with other tracking methods.
Browser extensions may use web accessible resources; not all do, but thousands use these resources. These resources, for instance images, may be accessed by websites that are loaded in the browser. The developer of the extension needs to declare web accessible resources explicitly in the manifest.
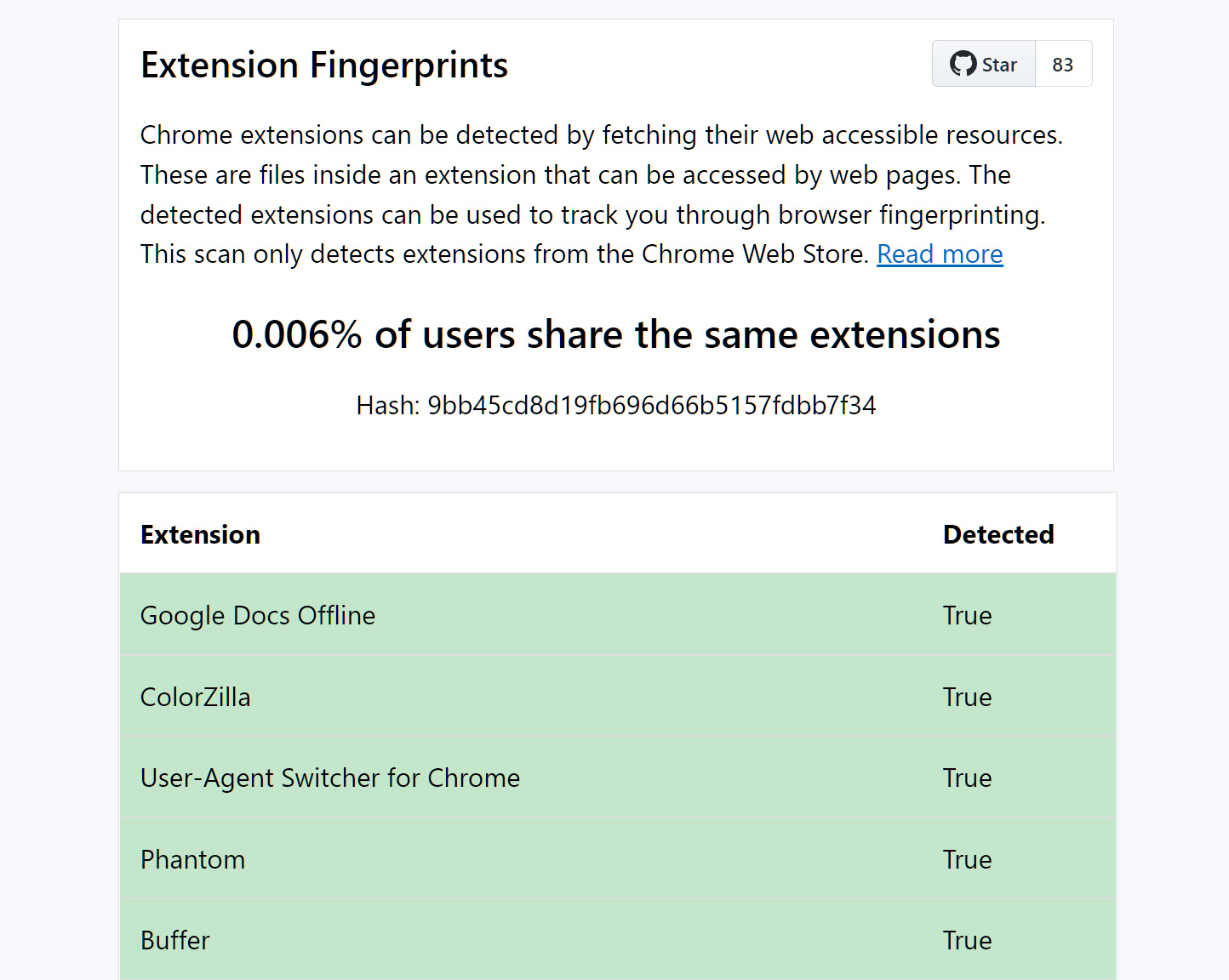
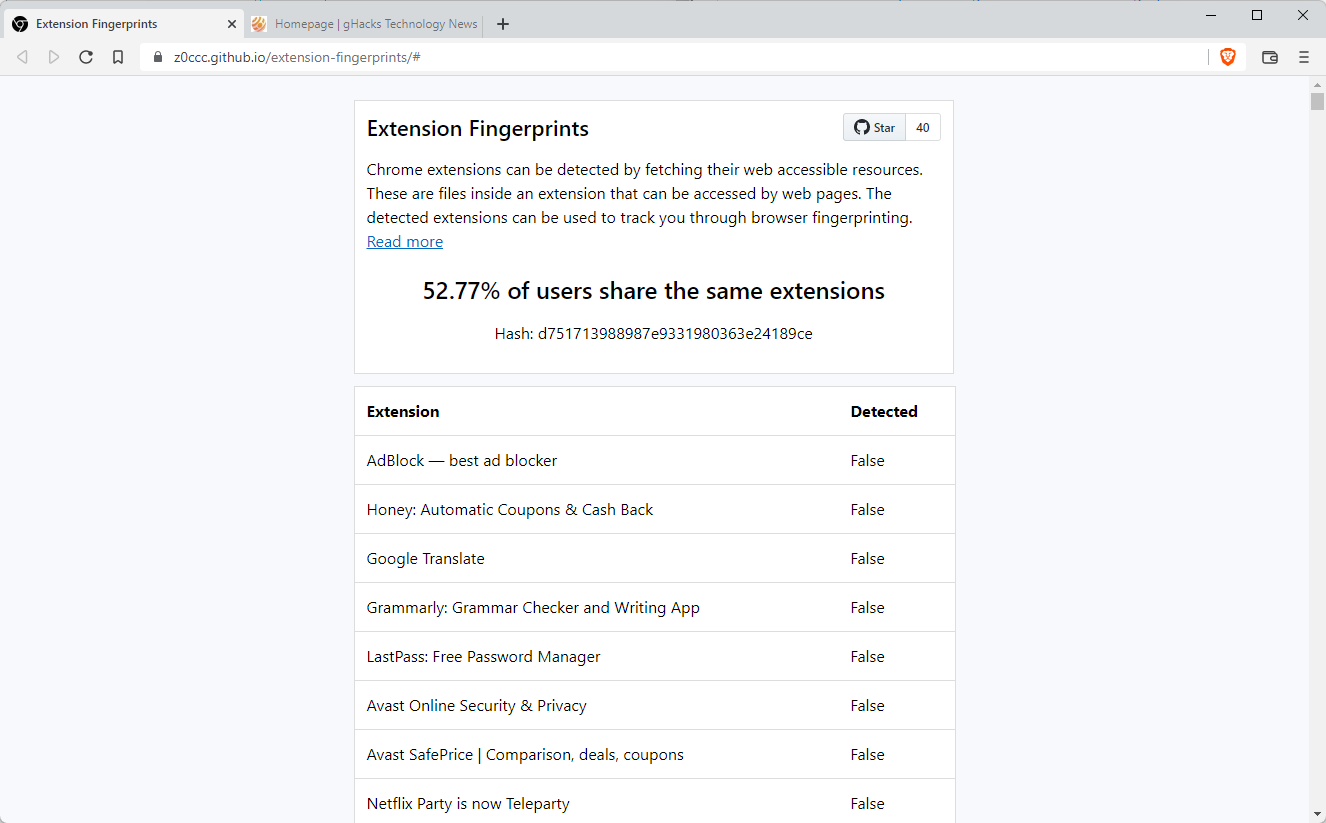
Extension Fingerprints is an open source script that checks whether these extensions are installed in the user's browser. The developer added scans for over 1000 extensions to the script, which are the most popular ones from a user installation point of view. Popular browser extensions such as Google Translate, Honey, Avast Online Security & Privacy, Malwarebytes Browser Guard, LastPass, Cisco Webex Extension, DuckDuckGo Privacy Essentials, or Amazon Assistant for Chrome use web accessible resources.
The list can be extended to add extensions with less than 70,000 users to the mix, which would improve detections and fingerprinting.
Point your web browser to this page to run the browser fingerprinting test. The script that runs on the page checks for the existence of web accessible resources and uses the information to return how unique the fingerprint is.
The browser's fingerprint is shared with the majority of users if none of the extensions that the script scans for is installed.

Your installed browser extension may be used to fingerprint you - gHacks Tech News
Websites may detect if certain browser extensions are installed; the information may be used to fingerprint the user of the browser.
www.ghacks.net